Within the Competence Center Quantum Computing Baden-Württemberg, collaborative projects are funded by the Ministry of Economics, Labor and Tourism Baden-Württemberg. Five projects are being funded in the second project period from 2023 to 2024:
Joint Projects within the Competence Center Quantum Computing
QC4BW II — Development and benchmarking of a diamond-based spintronic quantum register for an upscalable quantum processor II

The aim of the project is to develop a diamond-based, spintronic quantum register for a scalable quantum processor to evaluate quantum chemical processes. Building on the successful first phase of the project, the performance of the QC processor developed therein will be increased by means of further hardware development and more efficient quantum algorithms.
Partners: Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics IAF; Fraunhofer Institute for Chemical Technology ICT; Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Institute for Condensed Matter Theory; Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Institute of Physics; University of Konstanz, Department of Physics; University of Stuttgart, 3rd Institute of Physics; University of Ulm, Institute of Quantum Optics.
Associated partners: Diamond Materials GmbH; Evatec Europe GmbH; HQS Quantum Simulations GmbH; IBM Deutschland GmbH; Merck KGaA; Q.ANT GmbH; Qinu GmbH; Quantum Brilliance GmbH; Robert Bosch GmbH; SVA System Vertrieb Alexander GmbH; Swabian Instruments GmbH
Find more information about the project here.
QORA II — Quantum optimization with resilient algorithms II

Companies increasingly have to manage large and complex portfolios even outside the financial sector. The ability to make optimal decisions quickly is becoming a key competitive advantage. In the future, quantum computers will be able to outperform conventional computers in optimization processes. In the follow-up project “QORA II,” the knowledge gained so far about the optimization algorithms required for this will be deepened and extended.
Partners: Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics IAF; Fraunhofer Institute for Industrial Engineering IAO; Baden-Württemberg Cooperative State University, Ravensburg; University of Tübingen, Institute for Theoretical Physics; University of Konstanz, Department of Physics; University of Stuttgart, Institute for Functional Matter and Quantum Technology; University of Stuttgart, Institute of Computer Engineering
Associated partners: Airbus Defence and Space GmbH; Bausparkasse Schwäbisch Hall AG; HQS Quantum Simulations GmbH; JoS Quantum GmbH; Landesbank Baden-Württemberg; Thales Deutschland GmbH; Wüstenrot & Württembergische AG
Find more information about the project here.
SEQUOIA End-to-End — Transparent quantum software engineering and algorithm design of application-centric end-to-end solutions

The main goal of the joint research project SEQUOIA End-to-End is to make today’s bottlenecks in the entire quantum software development process transparent and to explore and provide performant, automated and controllable end-to-end solutions for industrial use cases through holistic quantum software engineering.
Partner: Fraunhofer Institute for Industrial Engineering IAO; Fraunhofer Institute for Manufacturing Engineering and Automation IPA; Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics IAF; Fraunhofer Institute for High-Speed Dynamics Ernst-Mach-Institut EMI; Eberhard Karls University Tübingen - Chair Embedded Systems; FZI Research Center for Information Technology; University of Stuttgart - Institute for High Performance Computing HLRS; Albert Ludwigs University Freiburg - Chair of Theoretical Physics; Karlsruhe Institute of Technology - Institute for Information Security and Reliability
Associated partners: Accenture GmbH; Adesso SE; Anaqor; Bertrandt Technikum GmbH; Bundesdruckerei GmbH; Classiq; DB Systel GmbH; Denso AUTOMOTIVE Deutschland GmbH, Dürr Systems AG; Hays AG; HQS Quantum Simulations GmbH; IBM Deutschland GmbH; Komm.ONE AöR; KUMAVISION AG; Leichtbau BW GmbH; Marquardt GmbH; Pfizer Manufacturing Deutschland GmbH; Planerio GmbH; PlanQK Projekt; P3 group GmbH; regio iT gesellschaft für informationstechnologie mbh; Reuter Technologie GmbH; Schwartz IT KG; Simerics GmbH; TRUMPF Werkzeugmaschinen GmbH + Co. KG; Überlandwerk Mittelbaden GmbH & Co. KG; Verband Deutscher Maschinen- und Anlagenbau e.V.; VINCI Energies Services GmbH; Volkswagen AG; Zeppelin GmbH
Find more information about the project here.
SiQuRe II — Modeling and simulation of NV-based qubit registers II
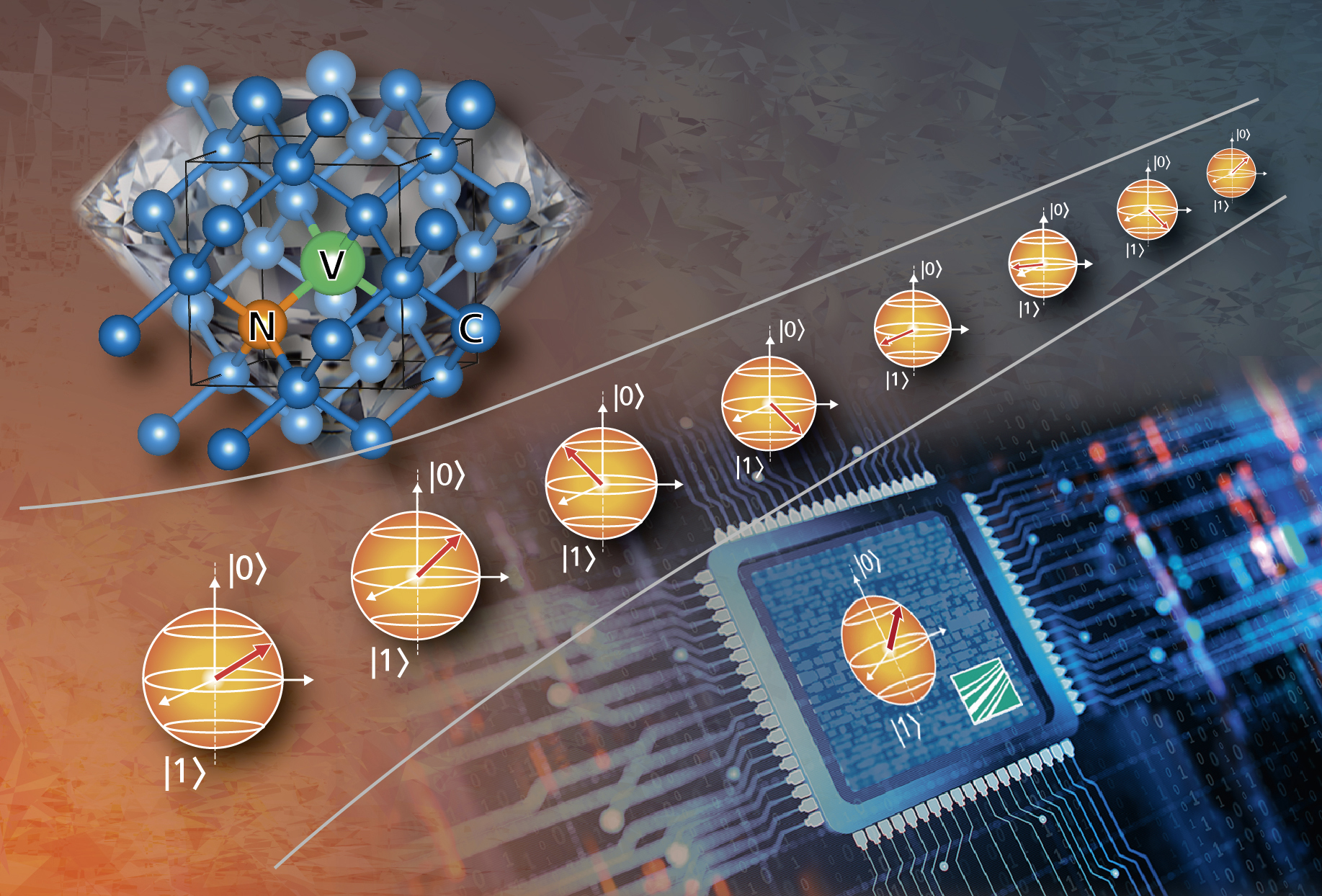
Using models and computer simulation methods of theoretical quantum physics, the research project addresses the question under which conditions a coupled spin system consisting of NV centers and some 13C atoms exhibits robust quantum states that can be used as a qubit system for the construction of solid-state-based quantum computers. Characterization and certification of essential quantum properties, such as entanglement content, will be explored with respect to scalability.
Partners: Fraunhofer Institute for Mechanics of Materials IWM; Albert Ludwigs University Freiburg, Institute of Physics; University of Ulm, Institute for Complex Quantum Systems
Associated partners: Carl Zeiss SMT GmbH, JoS Quantum GmbH, MTU Aero Engines AG, NVision, Tensor AI Solutions GmbH
QuESt+ — IBM quantum computing: material design for electrochemical energy storage and conversion using innovative simulation techniques
In the QuESt+ project, the IBM quantum computer is used for the application-oriented further development of material simulations for electrochemical energy systems. The aim of the follow-up project QuESt+ is to deepen and improve the knowledge gained so far on the simulation of electrochemical processes for the realization of sustainable energy sources. The focus is on the application of error mitigation strategies as well as the further development of quantum computing algorithms and the solution of partial differential equations.
Partners: Fraunhofer Institute for Mechanics of Materials IWM; DLR Institute for Quantum Technologies QT; DLR Institute for Technical Thermodynamics; Helmholtz Institute Ulm HIU
Associated partners: Mercedes-Benz Group AG, Robert Bosch GmbH
 Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics IAF
Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics IAF